The significance of proton pump inhibitors for acid reflux.
The Role of Proton Pump Inhibitors in Managing Acid Reflux
Acid reflux, commonly referred to as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), represents a medical condition characterized by the backward movement of stomach acid into the esophagus. This backward flow of acid can result in symptoms such as heartburn, regurgitation, and an overall sense of discomfort in the chest or throat area. The treatment for GERD has evolved significantly over the years, with proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) emerging as a central component in managing its symptoms.
Understanding Proton Pump Inhibitors
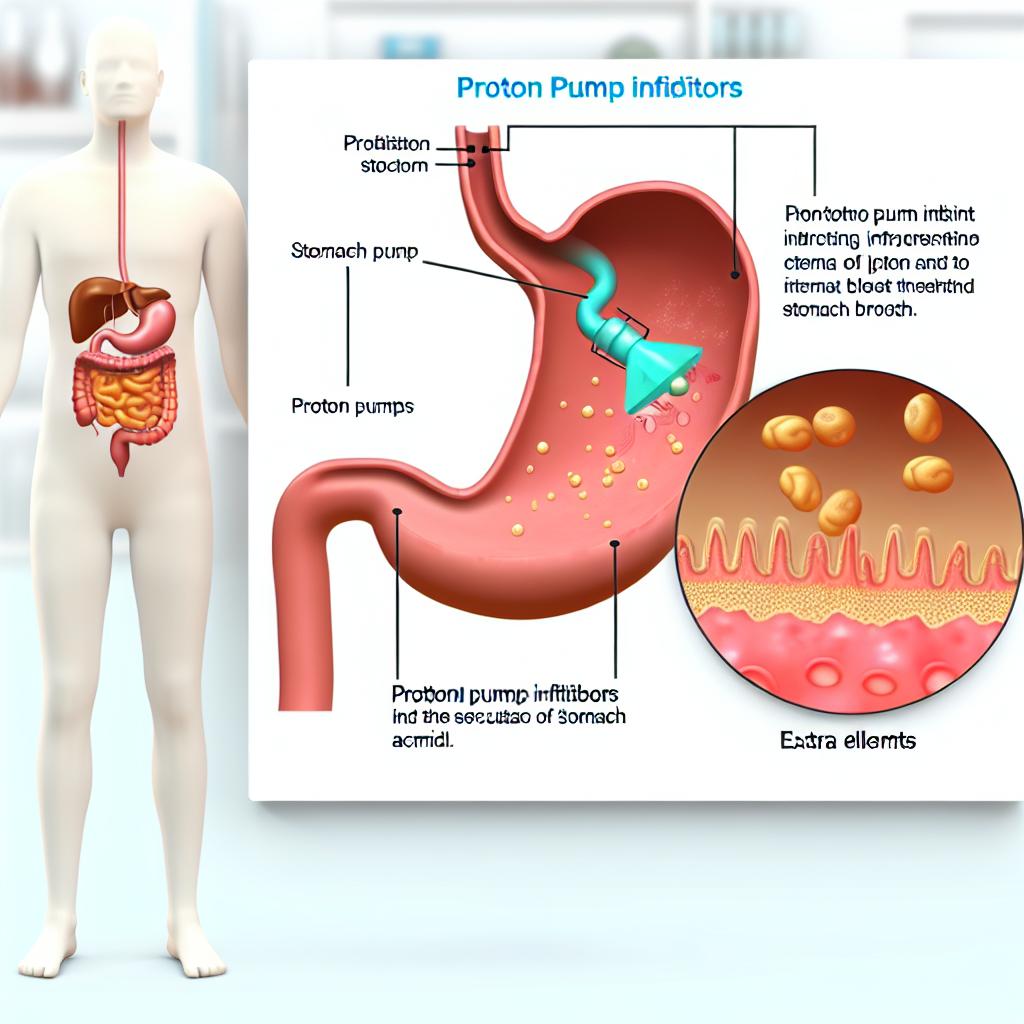
Proton pump inhibitors are a specialized group of medications specifically designed to curb the production of stomach acid. By effectively blocking the proton pumps in the stomach lining, these drugs suppress the secretion of acid, which constitutes a crucial step in controlling GERD symptoms. Notable examples of PPIs include omeprazole, lansoprazole, and esomeprazole. Given their targeted action, PPIs are often prescribed for individuals exhibiting severe or chronic forms of acid reflux, providing much-needed relief and facilitating esophageal healing.
Mechanism of Action
PPIs work by irreversibly binding to the hydrogen/potassium ATPase enzyme system, commonly known as the proton pump, located in the lining of the stomach. This binding inhibits the final step in the gastric acid production pathway, leading to a significant decrease in acid secretion. Unlike other acid-reducing medications, such as antacids that neutralize existent acid after secretion, PPIs are preventive, addressing acid production at its source.
Benefits of Proton Pump Inhibitors
The primary advantage of employing PPIs lies in their ability to significantly reduce stomach acid production, which subsequently alleviates the discomfort associated with acid reflux. By suppressing acid levels, PPIs enable the esophagus to regenerate and recover from the erosive damage of stomach acid. This therapeutic effect is critical, especially for individuals experiencing frequent or intense GERD symptoms. Furthermore, PPIs also play a preventive role, warding off complications such as esophageal strictures and Barrett’s esophagus—a precancerous condition that arises due to prolonged acid exposure and inflammation.
Enhanced Quality of Life
The deployment of PPIs can transform the lives of individuals suffering from chronic GERD. By minimizing acid reflux and associated symptoms, these medications help restore normalcy, allowing patients to partake in daily activities without the constant presence of discomfort. Many report improved sleep, enhanced dietary choices, and a general increase in life satisfaction upon finding adequate management of their condition through PPIs.
Effectiveness of Treatment
The efficacy of PPIs in treating GERD symptoms is well-supported by clinical research. Numerous studies have highlighted the capacity of PPIs to provide rapid relief from symptoms, with most individuals noting substantial improvement within just a few days after commencing treatment. For certain patients, especially those with persistent symptoms, prolonged use of PPIs may be essential to ensure continued symptom control.
Adherence to Medical Guidance
It is imperative for patients to adhere to the prescribed duration and dosage of PPI treatment as advised by their healthcare provider. Deviations from medical guidance can potentially diminish the effectiveness of therapy or increase the risk of adverse effects. Patients should engage in open dialogue with their healthcare providers, making sure they communicate any ongoing symptoms or concerns, which can assist in tailoring the treatment plan to their specific needs.
Potential Side Effects and Considerations
While PPIs are generally recognized as safe and effective, they are not devoid of potential side effects. Patients may experience mild side effects such as headache, diarrhea, or nausea. The discussion about any side effects should be transparent, encouraging patients to report persisting issues to their healthcare providers promptly.
Risks of Long-term Use
Extended use of PPIs has been linked to an increased risk of several health issues including bone fractures, kidney disease, and vitamin B12 deficiency. Therefore, it is crucial to evaluate the potential benefits and risks associated with long-term PPI usage. Patients and providers should engage in regular reviews of ongoing necessity, adjusting treatment approaches if and when appropriate to mitigate risk.
Conclusion
Proton pump inhibitors hold a distinguished position in the management of acid reflux, providing significant symptomatic relief and esophageal protection. However, the decision to initiate, continue, or modify PPI therapy should be made collaboratively with healthcare providers, taking into account individual patient factors and the evolving landscape of GERD management strategies. For those seeking more comprehensive information about managing acid reflux, consultations with medical professionals or referencing authoritative health sources are recommended. This ensures that decisions are well-informed and conducive to optimal health outcomes, tailored to suit individual circumstances and health profiles.
